A perspective on user management from all angles of IT
Covering Windows, Linux, Mac, Mobile (android/iOS) and discussion on what else should be user access controlled for optimum security
The importance of User Access Control in 2023 for Cyber Security by implementing security measures is critical for managing user access.
Contents
Stuff this is covered about User Access Control in this blog post:
- A perspective on user management from all angles of IT
- What is User access control?
- Benefits of UAC
- IT Job Roles that administer User Access Controls
- Who is responsible for User Access Control?
- Is User Access Control best managed in-house in 2023?
- IT Procedures to maintain User Access
- Managing User Access for Cybersecurity with: Active Directory
- Why manage UAC with Active Directory?
- Setting up permissions with Active Directory
- With the right tools and processes in place, organizations can take control of user access and protect their data from unauthorized access.
- Analysing UAC with as Security Information and Event Management
- User Access Control In Linux OS
- Permissions in Linux
- Groups in Linux
- sudo command
- Setting permissions
- Managing user access-
- What else should be User Access Controlled
- Other than Windows, Linux and mobile devices
- it is important for organizations to have a strategy in place for controlling access to their IT resources, regardless of the platform or technology being used. By implementing the right controls and solutions, organizations can protect their data from unauthorized access and ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive information. 10
- Mobile Device Management:
- What about User Access Control on your company mobile phones?
Access Control in 2023
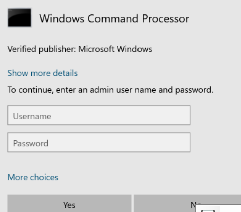
Typically, UAC is a prompt that is displayed on a Windows Operating system when an elevation of privileges are requested by a standard user without privilege to a local or network resource.
UAC stands for User Account Control in Windows OS Family
It is a security feature designed to prevent unauthorized changes to the system and to help protect the computer from malicious software.
UAC works by requiring users to provide administrative approval before making changes to the computer. When a user tries to perform an action that requires administrative privileges, UAC displays a prompt asking for confirmation. The user must provide the necessary credentials or confirm the action before it can proceed.
UAC helps to prevent malicious software from making unauthorized changes to the system without the user’s knowledge or consent. It also helps to ensure that users are aware of the changes they are making to the system and can make informed decisions about whether to proceed.
In Windows, UAC can be managed and configured through the User Accounts control panel or through Group Policy settings. The level of UAC can be adjusted to suit the needs of the organization, with options ranging from full administrative access to strict restrictions on what actions users can perform.
What is User access control?
.. is the process of managing and controlling access to systems and data by users.
This includes setting up and managing user accounts, defining access levels and permissions, and implementing security measures such as authentication and multi-factor authentication.
A user access control process typically includes steps such as creating and managing user accounts, setting up access levels and permissions, and implementing security measures such as authentication and multi-factor authentication. This process can be automated to minimize the time and effort required to manage user access.
It is important to have a user access control process in place, as it helps to prevent unauthorized access to systems and data. By managing and controlling access to systems and data, organizations can reduce their risk of a security incident.
In addition to managing and controlling user access, organizations should also regularly review user accounts and access levels to ensure that they are still needed and that the access level is appropriate. This includes monitoring for inactive accounts, removing or disabling accounts that are no longer needed and revoking access for users that have left the organization.
In summary, User access control is a critical aspect of IT security, it helps to prevent unauthorized access to systems and data. Organizations should have a process in place to create and manage user accounts, set up access levels and permissions, and implement security measures such as authentication and multi-factor authentication. It is also important to regularly review user accounts and access levels to ensure that they are still needed and that the access level is appropriate.
Benefits of UAC
The proper management of user access is an important aspect of IT security and has several benefits, including:
- Improved security:
By controlling who has access to sensitive information and resources, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. - Better data management:
Proper user access management can help ensure that sensitive data is only accessed by authorized individuals and used in accordance with established policies and procedures. - Compliance with regulations:
User access management helps organizations comply with regulations and standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), by providing evidence of who has access to what data and how it is being used. - Efficient resource utilization:
By controlling who has access to resources such as servers, applications, and databases, organizations can ensure that these resources are used efficiently and effectively. - Increased accountability:
With proper user access management, organizations can keep track of who has access to sensitive information and resources and hold users accountable for their actions.
In summary, managing user access provides organizations with improved security, data management, regulatory compliance, efficient resource utilization, and increased accountability, making it a critical component of an effective IT security strategy.
IT Job Roles that administer User Access Controls
Before we dive into how too manage user access control, let’s quickly cover the job roles today responsible for ensuring to good compliance standards, scrutinising and analysing systems to maintain good practices User Access Control
User Access Control (UAC) is a absolutely critical aspect of IT management, all IT managers or of similar position, must ensure secure access to sensitive information, systems, and data – providing their team with adequate tools, knowledge and IT procedures to follow in order to maintain user control
Who is responsible for User Access Control?
the IT department to manage and configure user access controls in different environments.
The proper implementation of UAC is crucial in protecting sensitive information and ensuring the smooth operation of IT systems.
IT System Technicians are responsible for the implementation of UAC, but their level of skill and expertise varies depending on their job role and responsibilities.
Security Analysts, for instance, are responsible for the overall security of the system and are expected to have a higher level of expertise in configuring UAC. Meanwhile:
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3 technicians have varying levels of expertise in handling UAC and are responsible for different aspects of the system.
Is User Access Control best managed in-house in 2023?
In-house IT technicians are often preferred by businesses as they are more familiar with the local environment and can respond quickly to any issues that may arise. On the other hand, outsourcing IT can also be a viable option, especially for small businesses that cannot afford to hire a full-time IT team. However, businesses must be cautious when outsourcing IT to ensure that their user information is not being transmitted overseas, which may lead to security breaches.
Regardless of whether a business opts for in-house IT or outsourced IT, it is crucial for every admin to be conscious about user information and accuracy. This is because incorrect or inaccurate information can lead to security breaches and put the entire system at risk. Therefore, every admin should make sure that the user information entered is accurate and up-to-date to ensure the smooth operation of the system.
IT Procedures to maintain User Access
From creation of user accounts, to decommissioning accounts …
Sys Admins alike should ensure all accounts are disabled with trackability (in a service request/or help desk Ticket) – logging removal or addition of group membership permissions within AD , conversion of mailboxes to Shared, any changes of licensing, notification to third party software / or business admins running CRMs for account management outside of Windows Domain not controlled by IT
e.g. Marketing (WordPress, SalesForce). Some organisations may have in-house apps which aren’t linked to AD – and will not recognize their disabled state, so informing other departments is always a great way to ensure secure access controls are being adhered too from IT departments.
Unblocking user accounts with Risky Sign Ins (azure AD/365) – should be managed on another level than a low level Technician.
for example Phishing Emails can often trigger user blocks which may require Unblock by a Security Analyst, a helpdesk technician may not have the level of permission to do this (taken from experience working @ Durham University)
When a user falls victim to an Phishing Attack, typically they’re lead to cloned / specifically crafted and engineered webpage which will look like an Office 365 login page (any other service can be picked, Salesforce for example or Banks such as Barclays) … the page will compromises the credentials – it is then up to the IT team to respond to this security event.
In an ideal situation, the user will inform IT of their unfortunate action but this is not always the case. This is why monitoring of user sign in’s etc. is critical to maintain user access control.
Sometimes when a hacker manages to steal credentials using a a phishing attack, when they attempt to login using them – Azure AD Identify Management – for user access – will recognise the dodgy sign in attempt and disable the account. if procedures are not followed – and all considerations are checked – then a security Breach could occur.
Managing User Access for Cybersecurity with: Active Directory
Cybersecurity is a top concern for organizations today, and protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access is critical. User Access Control (UAC) is an important component of an overall cybersecurity strategy, and managing UAC with Active Directory (AD) is a powerful way to ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive information.
In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of managing UAC with AD and how to use Active Directory to set up permissions and control user access.
Manage User Access Control with Active Directory
Active Directory is a centralized database used to store information about users, computers, and other resources within an organization. By integrating UAC with AD, organizations can benefit from:
- Centralized management: Managing UAC with AD allows organizations to centralize the management of user access control, making it easier to enforce security policies and manage permissions for large groups of users.
- Scalability: AD is designed to scale as an organization grows, and by integrating UAC with AD, organizations can ensure that their security measures can grow with their user base.
- Improved security: By using AD to manage UAC, organizations can enforce security policies and control user access to sensitive information, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Setting up permissions with Active Directory
The following steps can be used to set up permissions and control user access with Active Directory:
- Create Active Directory user accounts: To control user access, organizations must first create Active Directory user accounts for each user in the organization. This will allow administrators to manage permissions and control access to sensitive information.
- Set up groups: Groups are a powerful way to manage user access, and organizations can use AD to create groups of users and set up permissions for each group.
- Assign permissions to groups: After creating groups, organizations can assign permissions to each group, such as the ability to read, write, or execute files and folders
. - Apply Group Policy Objects (GPOs): GPOs can be used to enforce UAC policies, adjust the level of UAC notification, and configure UAC settings for specific users or groups.
- Use the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) or Windows PowerShell: The GPMC or Windows PowerShell can be used to manage UAC settings in an AD domain, allowing organizations to automate UAC management tasks and manage UAC settings for multiple computers in the domain.
In conclusion, managing User Access Control with Active Directory is an important component of a robust cybersecurity strategy. By integrating UAC with AD, organizations can centralize the management of user access, enforce security policies, and improve the security of their sensitive information.
With the right tools and processes in place, organizations can take control of user access and protect their data from unauthorized access.

Security Certifications
Cyber Essentials Plus is a certification program for organizations to demonstrate their commitment to cybersecurity.
Read more about this certification here: https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/cyberessentials/overview
The technical controls for User Access Control in Cyber Essentials Plus include the following:
- User accounts:
Organizations must have a process for creating, managing, and disabling user accounts. This includes setting strong passwords, regularly monitoring account activity, and disabling inactive accounts. - Access control:
Organizations must implement access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control, to limit user access to only the systems and data they need to perform their job. - Authentication:
Organizations must implement strong authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication, to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive information. - User privileges:
Organizations must implement least privilege principles, where users are only given the minimum privileges necessary to perform their job. - Session management:
Organizations must implement session management controls, such as automatic logoff, to prevent unauthorized access to user sessions. - Remote access:
Organizations must secure remote access to the network, such as by using a Virtual Private Network (VPN), to ensure that remote users can access the network securely
. - Passwords:
Organizations must implement password policies, such as setting strong passwords, regularly changing passwords, and preventing the reuse of passwords, to secure user accounts. - User education:
Organizations must educate users on the importance of security and best practices for protecting sensitive information.
These technical controls are designed to help organizations secure user access and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. By implementing these controls, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to cybersecurity and protect their sensitive information from cyber threats.
Analysing UAC with as Security Information and Event Management
SEIM stands for Security Information and Event Management, which refers to a set of technologies and processes used to manage and analyse security-related data generated by various devices and systems within an organization. SEIM tools are commonly used to monitor and analyse security events, identify security threats, and provide alerts to IT administrators.
In 2023, the popular SEIM software can be found from this daft list here, to learn more about – many courses are available on LinkedIn Learning +Microsoft Learn:
- Splunk
- ArcSight
- LogRhythm
- RSA NetWitness
- QRadar
- Graylog
- Logstash
- Sumo Logic
- SolarWinds Log Manager
- Elastic Stack.
To manage User Access Control (UAC) in Windows, SEIM tools can be used in conjunction with the UAC features in Windows to provide enhanced security and event management. SEIM tools can be used to:
- Monitor UAC events:
SEIM tools can be used to monitor UAC events such as user logons and UAC prompts, and to alert administrators to potential security issues or policy violations. - Analyse UAC data:
SEIM tools can be used to analyse data generated by UAC, such as the number of UAC prompts or the frequency of UAC-related events, to help identify trends and potential security risks. - Correlate
UAC events with other security events: SEIM tools can be used to correlate UAC events with other security events from other sources, such as firewall logs or intrusion detection systems, to provide a more complete picture of the security posture of the organization. - Generate reports and dashboards:
SEIM tools can be used to generate reports and dashboards that provide insight into UAC-related events and trends, and help IT administrators make informed decisions about UAC policies and management.
Any SEIM tool can be used in conjunction with UAC in Windows to provide enhanced security and event management, helping organizations to better understand their security posture and respond to security events more effectively.
User Access Control In Linux OS
In Linux operating systems, UAC is implemented through the use of permissions and groups.
Permissions in Linux
In Linux, every file and directory has a set of permissions that control who can read, write, and execute the files or directories. These permissions can be set for the owner of the file, the group owner, and others. By using permissions, Linux administrators can control who has access to sensitive information and resources.
Groups in Linux
In Linux, groups are used to manage user access to resources. Users can be added to groups, and permissions can be set for each group. For example, a group of users can be granted access to a specific file or directory, and each member of the group will have the same level of access to that resource.
sudo command
The sudo command is used to grant users temporary administrative privileges. This allows users to perform administrative tasks, such as installing software or modifying system settings, without logging in as the root user. The sudo command is a powerful tool for managing user access, as it allows administrators to grant users access to sensitive information and resources, while still maintaining control over who has access.
Setting permissions
In Linux, permissions can be set using the chmod command. This command allows administrators to change the permissions on a file or directory. For example, the following command can be used to grant full permissions to the owner of a file and read-only access to others:
chmod 755 filenameManaging user access-
To manage user access in Linux, administrators can use tools such as the usermod command, which allows administrators to add or remove users from groups, and the visudo command, which allows administrators to edit the sudoers file and control who has access to the sudo command.
By using permissions, groups, and the sudo command, administrators can control who has access to sensitive information and resources, ensuring that only authorized users have access.
What else should be User Access Controlled
Other than Windows, Linux and mobile devices
In addition to Windows and Linux operating systems, there are several other platforms and technologies that require user access control.
Other platforms and technologies that require user access control:
- Cloud Services:
Cloud services such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) all have user access controls built into their platforms. This allows administrators to control who has access to the cloud resources and what actions they can perform. - Network Devices:
Network devices such as routers, switches, and firewalls also have user access controls that can be used to control who has access to the device and what actions they can perform. - Databases:
Databases such as Oracle, MySQL, and Microsoft SQL Server also have user access controls that can be used to control who has access to the database and what actions they can perform. - Virtualization Platforms:
Virtualization platforms such as VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V also have user access controls that can be used to control who has access to the virtual environment and what actions they can perform. - Containerization Platforms:
Containerization platforms such as Docker and Kubernetes also have user access controls that can be used to control who has access to the containers and what actions they can perform.
In addition to these platforms and technologies, there are also several tools and solutions that can be used to manage user access control across different platforms and technologies. Examples of these tools include identity and access management (IAM) solutions, single sign-on (SSO) solutions, and directory services such as Microsoft Active Directory.
it is important for organizations to have a strategy in place for controlling access to their IT resources, regardless of the platform or technology being used. By implementing the right controls and solutions, organizations can protect their data from unauthorized access and ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive information.
Mobile Device Management:
What about User Access Control on your company mobile phones?
Mobile device management (MDM) solutions can be used to manage user access control on company mobile phones. MDM solutions provide a way for organizations to manage the security and configuration of their mobile devices, including setting policies for user access control.
Common methods of Access Control in 2023 for Company Mobile Phones
Common ways that Mobile Device Management software can be used for user access control consist of:
- Password and Screen Lock:
MDM solutions can enforce password policies, such as requiring strong passwords, and screen lock policies, such as setting a timeout for when the screen will lock. This helps to ensure that only authorized users have access to the device. - Remote
Wipe: MDM solutions can be used to remotely wipe a device if it is lost or stolen. This helps to protect sensitive company data that may be stored on the device. - App Management:
MDM solutions can be used to control which apps are installed on a device, and to restrict access to specific apps based on user roles. This helps to ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive company information. - Network Access Control:
MDM solutions can be used to control which networks the device can connect to, and to restrict access to specific networks based on user roles. This helps to ensure that the device is only connecting to secure networks. - Device Configuration:
MDM solutions can be used to set configuration policies for devices, such as enforcing encryption policies, and to enforce security settings, such as disabling the camera.
Conclusion
In conclusion, MDM solutions provide a way for organizations to manage user access control on company mobile phones, ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive information, and that the devices are secure and configured in a way that meets the organization’s security needs.
By implementing an MDM solution, organizations can help to protect their data and maintain control over their mobile devices and provide compliance for Cyber Security Audits such as CE+, a good choice is Sophos Central for MDM in 2023.
Join Our Community!
🌟 Get exclusive insights and the latest IT tools and scripts, straight to your inbox.
🔒 We respect your privacy. Unsubscribe at any time.
